_____ Refers to the Conversion of Glucose to Glycogen.
Hypoglycemia is a health condition that refers to low blood sugar glucose levels. The liver plays a major role in carbohydrate homeostasis controlling glucose levels by synthesizing and degrading glycogen and making glucose via gluconeogenesis.
How Is Glycogen Converted To Glucose Quora
Glycogen is synthesized depending on the demand for glucose and ATP energy.
. Glycogen Carbohydrates. Mutant muscle glycogen phosphorylase is unable to bind to glucose 6-phosphate. C without the use of oxygen.
Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. During any amount of intense activities your body will use carbohydrates for energy. A without the involvement of ADP.
Other than that yes glycolysis is glucose to pyruvate. Glucose sparing refers to the use of noncarbohydrate fuel molecules in the post absorptive state. One is found in the blood stream while the other comes from your muscles and liver.
There will be a rise in intracellular levels of glucose 6 phosphate in fat skeletal muscle and liver due to a high concentration of blood glucose. The first is a linear pathway where the hexose skeleton remains intact and is commonly known as the direct pathway the direct pathway refers to the conversion of glucose to glycogen via the. Refer to the Biochemistry in Focus section of your text for this chapter to answer this question.
Topper and Stetten 1 fed n-galactose-l-Cl4 by stomach tube. True Carbohydrate and fat pools are oxidized directly to produce cellular energy but amino acid pools must first be converted to a carbohydrate intermediate before being sent through cellular respiration pathways. B without the use of glycogen.
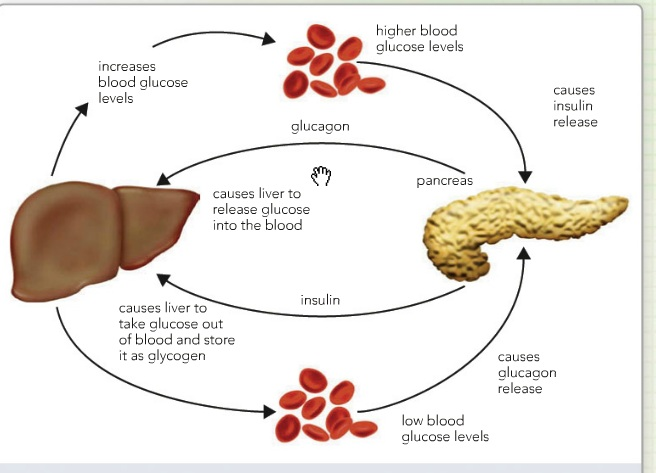
The islets of Langerhans in the pancreas secrete a hormone called insulin. Glycogen or glucose to pyruvate or acetyl CoA. E by the conversion of pyruvate to lactate.
Discuss what effect does this conversion have on the cells ability to acquire more glucose. This process occurs when prolonged fasting occurs and the body does not receive any external nutrition for a long time. Gluconeogenesis refers to a group of metabolic reactions some of them highly exergonic and irreversible which are regulated both locally and globally by insulin glucagon and cortisol.
Which of the following is a waste product of the aerobic glucose metabolism. Start studying the ch 4 flashcards containing study terms like 2. As a single unit it is a much smaller molecule.
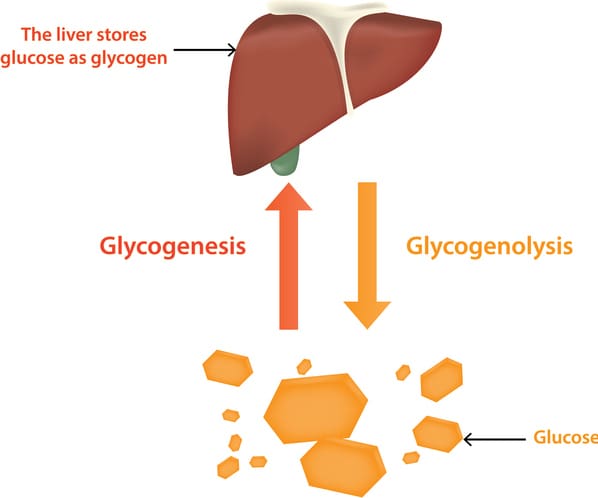
With a mutase it is converted to glu-6-p and can enter glycolysis from there. Glycogenolysis is from glycogen to glucose-1-P. Glycogenesis is the formation of glycogen from glucose.
The polymer is composed of units of glucose linked alpha 1-4 with branches occurring alpha 1-6 approximately every 8-12 residues. First individual glucose molecules are hydrolyzed from the chain followed by the addition of a phosphate. Glycogen refers to glycogen whereas Lysis refers to the process of breakdown.
About 90 per cent of the Cl4 was in C-l of the glucose unit of. The purpose of this system localized in both the cytosol and mitochondria is to maintain blood glucose level constant throughout fasting state. The body uses these molecules to help sustain itself.
In addition glycogen is a type of Carbohydrate. Anaerobic metabolism refers to the generation of ATP. Glycogen is a highly branched polymeric structure containing glucose as the basic monomer.
Glucagonwhich is secreted by the pancreas gland in humans is responsible for converting glycogen to glucosethere are 2 hormones that could convert glycogen to glucose. This process is activated during rest periods following the Cori cycle in the liver and also activated by insulin in response to high glucose levels. The process by which glucose is synthesised from non carbohydrate carbon source that mainly occurs in the liver is called as gluconeogenesisThe source or substrates of carbon for gluconeogenesis could be lactate glycerol and amino acids In the process of gluconeogenesis pyruvate is converted back to glucose and is transferred back to our bloodstreamThis glucose.
To fasted rats and isolated glucose from the liver glycogen. Gluconeogenesis refers to the formation of glucose by basically inverting the reactions of glycolysis with three bypasses of essentially irreversible reactions. These carbohydrates are broken down into glucose and glycogen.
Glycogen is a polymer of glucose up to 120000 glucose residues and is a primary carbohydrate storage form in animals. E glucose or fatty acids to pyruvate or acetyl. In addition the liver has generally been assumed to be the main site of fructose metabolism Caliceti et al 2017.
Glucose is usually broken down to a. The transport of glucose into the cell occurs by facilitated diffusion. Provide energy ATP for the working cells.
Step by step answerGlycogenolysis is the breakdown of Glycogen into Glucose. If both are present in relatively high amounts then the excess of insulin promotes the glucose conversion into glycogen for. If the glucose content increases from normal levels 70-100 mg per 100ml of blood insulin induces the uptake of excess glucose by the liver for the.
Mutant muscle glycogen phosphorylase is unable to convert to Question. D in the absence of available oxygen. The process of glucose converting to glycogen is called B.
Importance of glucose 6-phosphate in Glycogen Synthase. Learn about the definition of. D-glucose ATP - D-glucose-6-phosphate ADP ΔG The above reaction illustrates the conversion of D-Glucose to D-glucose 6-phosphate.
Jegatheesan and De Bandt 2017. The end of the molecule containing a free carbon number one on glucose is called a reducing. The conversion of glucose into glycogen and glycogen back into glucose is entirely under the control of hormones.
Glycogenesis is the formation of glycogen from glucose. Glucose and glycogen are both carbohydrates but glucose is classified as a monosaccharide and sugar. According to Virtual Chembook at Elmhurst College glycogen is classified as a complex carbohydrate and starch and its made up of several glucose molecules.
Mostly glycogenesis occurs in the liver. If both are present in relatively high amounts then the excess of insulin promotes the glucose conversion into glycogen for storage in liver and muscle cells. Glycogenesis is the process of glycogen synthesis in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage.
Glycogen is synthesized depending on the demand for glucose and ATP energy. Once glucose enters the cell it is rapidly converted into another molecule such as glucose-6-phosphate or glycogen.

Glycogenolysis Biochemistry Britannica

Glycogenesis Cycle Steps Significance Vs Gluconeogenesis Laboratoryinfo Com
No comments for "_____ Refers to the Conversion of Glucose to Glycogen."
Post a Comment